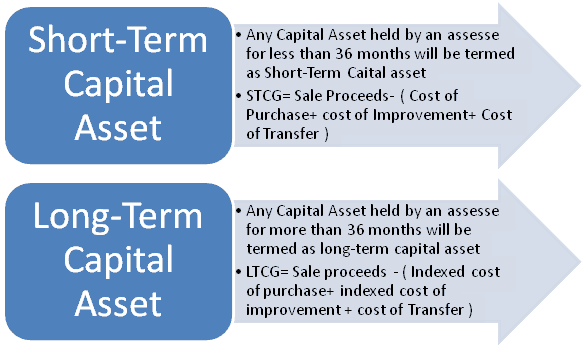
Short term capital gains rate real estate
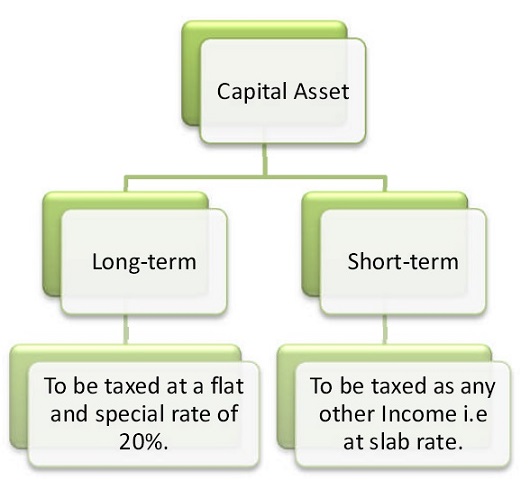
In the United States of America, individuals and corporations pay U. The tax rate depends on both the investor's tax bracket and the amount of time the investment was held. Short-term capital gains are taxed at the investor's ordinary income tax rate and are defined as investments held for a year or less before being sold.
Long-term capital gainson dispositions of assets held for more than one year, are taxed at a lower rate. As ofthe United States taxes short-term capital gains at the same rate as it taxes ordinary income. Long-term capital gains are taxed at generally lower rates, shown in color in the table below:.
Capital gains do not push ordinary income into a higher income bracket. The Capital Gains and Qualified Dividends Worksheet in the Form instructions specifies a calculation that treats both long-term capital gains and qualified dividends as though they were the last income received, then applies the preferential tax rate as shown in the above table.
The capital gain that is taxed is the excess of the sale price over the cost basis of the asset. The taxpayer reduces the sale price and increases the cost basis reducing the capital gain on which tax is due to reflect transaction costs such as brokerage fees, certain legal fees, and the transaction tax on sales.
In contrast, when a business is entitled to a depreciation deduction on an asset used in the business such as for each year's wear on a piece of machineryit reduces the cost basis of that asset by that amount, potentially to zero.
If the business then sells the asset for a gain that is, for more than its adjusted cost basisthis part of the gain is called depreciation recapture.
bankrate-logo
When selling certain real estate, it may be treated as capital gain. When selling equipment, however, depreciation recapture is generally taxed as ordinary income, not capital gain. Further, when selling some kinds of assets, none of the gain qualifies as capital gain. If a business develops and sells properties, gains are taxed as business income rather than investment income.
The Fifth Circuit Court of Appealsin Byram v. United Statesset out criteria for making this decision and determining whether income qualifies for treatment as a capital gain. Under the stepped-up basis rule, [8] for an individual who inherits a capital asset, the cost basis is "stepped up" to its fair market value of the property at the time of the inheritance. When eventually sold, the capital gain or loss is only the difference in value from this stepped-up basis.
Increase in value that occurred before the inheritance such as during the life of the decedent is never taxed. If a taxpayer realizes both capital gains and capital losses in the same year, the losses offset cancel out the gains. The amount remaining after offsetting is the net gain or net loss used in the calculation of taxable gains.
Any remaining net loss can be carried over and applied against gains in future years. However, losses from the sale of personal property, including a residence, do not qualify for this treatment.
Corporations with net losses of any size can re-file their tax forms for the previous three years and use the losses to offset gains reported in those years.
This results in a refund of capital gains taxes paid previously. After the carryback, a corporation can carry any unused portion of the loss forward for five years to offset future gains.
Corporations may declare that a payment to shareholders is a return of capital rather than a dividend. Dividends are taxable in the year that they are paid, while returns of capital work by decreasing the cost basis by the amount of the payment, and thus increasing the shareholder's eventual capital gain. Although most qualified dividends receive the same favorable tax treatment as long-term capital gains, the shareholder can defer taxation of a return of capital indefinitely by declining to sell the stock.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Capital Gains Tax - NerdWallet
From tocapital gains were taxed at ordinary rates, initially up to a maximum rate of 7 percent. The Tax Reform Act of repealed the exclusion of long-term gains, raising the maximum rate to 28 percent 33 percent for taxpayers subject to phaseouts. The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of caused the IRS to introduce FormSales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets, and to introduce radical changes to Form B. It was a temporary measure but was extended further through by the Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of as a jobs stimulus.
Inprovisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act "Obama-care" took effect that imposed the Medicare tax of 3. The following table summarizes the changes to the long-term capital gains tax rates made since Short-term capital gains have been taxed at the same rate as ordinary income for this entire period. Capital gains taxes are disproportionately paid by high-income households, since they are more likely to own assets that generate the taxable gains.
The disproportionate incidence on high-income households means that most debate on tax rates is partisan. The Republican Party favors lower rates, whereas the Democratic Party favors higher rates.
Even though the incidence of the tax is on high-income taxpayers, low-income taxpayers who do not file capital gains taxes may wind up paying them through changed prices as the actual payers pass through the cost of paying the tax. Another factor complicating the use of capital gains taxes to address income inequality is that capital gains are usually not recurring income. A taxpayer may be "high-income" in the single year in which he or she sells an asset or invention. The existence of the capital gains tax is controversial on partisan grounds.
Into support the Contract with America legislative program of House Speaker Newt GingrichStephen Moore and John Silvia wrote a study for the Cato Institute. In the study, they proposed halving of capital gains taxes, arguing that this move would "substantially raise tax collections and increase tax payments by the rich" and that it would increase economic growth and job creation.
They wrote that the tax "is so economically inefficient But publicly held companies have to pay corporate income tax Capital gains is a second tax on that income when the stock is sold. Richard Epstein says that the capital-gains tax "slows down the shift in wealth from less to more productive uses" by imposing a cost on the decision to shift assets. He favors repeal or "at the very least" a rollover provision to defer the tax on gains that are reinvested.
The fact that the long-term capital gains rate is lower than the rate on ordinary income is regarded by the political leftsuch as Sen. Bernie Sandersas a "tax break" that excuses investors make money online onlinedealsspotter com opportunity program work paying their "fair share.
Also, the lower rate partly compensates for the fact that some capital gains are illusory and reflect nothing but inflation between the time the asset is bought and the time it is sold. Moore writes, "when inflation is high The one-year threshold between short-term and long-term capital gains is arbitrary and has changed over time. Short-term gains are disparaged as speculation and are perceived as self-interested, myopic, and destabilizing, [27] while long-term gains are characterized as investmentwhich supposedly reflects a more stable commitment that is in the nation's interest.
Others call this a false dichotomy. There was special treatment of assets held for five years during the Presidency of George W. In her Presidential campaign, Hillary Clinton advocated holding periods of up to six years with a sliding scale of tax rates. Carried interest is the share of any profits that the general partners of private equity funds receive as compensation, despite not contributing any initial funds.
Thus, where the client realizes long-term capital gains, the manager's gain is a long-term capital gain—generally resulting in a lower tax rate for the manager than would be the case if the manager's income were not treated as a long-term capital gain.
Under this treatment, the tax on a long-term gain does not depend on how investors and managers divide the gain. This tax treatment is often called the "hedge-fund loophole", [32] even though it is private equity funds that benefit from the treatment; hedge funds usually do not have long-term gains. Warren Buffett has used the term "coddling the super rich". The capital gains tax raises money for government but penalizes investment by reducing the final rate of return.
Proposals to change the tax rate from the current rate are accompanied by predictions on how it will affect both results. For example, an increase of the tax rate would be more of a disincentive to invest in assets, but would seem to raise more money for government. However, the Laffer curve suggests that the revenue increase might not be linear and might even be a decrease, as Laffer's "economic effect" begins to outweigh the "arithmetic effect.
Another economic effect that might make receipts differ from those predicted is that the 24 virtual binary options game trading States competes for capital with other countries.
A change in the capital gains rate could attract more foreign investment, or drive United States investors to invest abroad. Congress sometimes directs the Congressional Budget Office CBO to estimate the effects of a bill to change the tax code. It is contentious on partisan grounds whether to direct the CBO short term capital gains rate real estate use dynamic scoring [39] to include economic effectsor static scoring that does not consider the 247 binary options demos effect on the incentives of taxpayers.
Republicans mandated dynamic scoring in the Budget and Accounting Transparency Act of Supporters of cuts in capital gains tax rates may argue that the current rate is on the falling side of the Laffer curve past a point of diminishing returns — that it is so high that its disincentive effect is dominant, and thus that a rate cut would "pay for itself.
Mark LaRochelle wrote on the conservative website Human Events that cutting the capital gains rate increases employment. He presented a U. Treasury chart to assert that "in general, capital gains taxes and GDP have an inverse relationship: He also cited statistical correlation based on tax rate changes during the presidencies of George W. BushBill Clintonand Ronald Reagan. However, comparing capital gains tax rates and economic growth in America from toBrookings Institution economist Leonard Burman found "no statistically the black keys money maker mp3 correlation between the two", even after using "lag times of five years.
Hungerford of the liberal Economic Policy Institute found "little or even a negative" correlation total money makeover message board capital gains tax reduction and rates of saving and investment, writing: This suggests that changing capital gains tax rates have had little effect on private saving".
Researchers usually use the top marginal tax rate to characterize policy as high-tax or low-tax. 1907 stock market crash figure measures the disincentive on the largest transactions per additional dollar of taxable income.
However, this might not tell the complete story. Roller coaster tycoon 2 make more money reason it is hard to prove correlation between the top capital gains rate and total economic output is that changes to the capital gains rate do not occur in isolation, but as part of a tax reform package.
They may be accompanied by other measures to boost investment, and Congressional consensus to do so may derive from an economic shock, from which the economy may have been recovering independent of tax reform.
The ability to use capital losses to offset capital gains in the same year is discussed above. Toward the end of a tax year, some investors sell assets that are worth less than the investor paid for them to obtain this tax benefit. A wash salein which the investor sells an asset and buys it or a similar asset right back, cannot be treated as a loss at all, although there are other potential tax benefits as consolation.
In January, a new tax year begins; if stock prices increase, analysts may attribute the increase to an absence of such end-of-year selling and say there is a January effect. A Santa Claus rally is an increase in stock prices at the end of the year, perhaps in anticipation of a January effect. A taxpayer can designate that a sale of corporate stock corresponds to a specified purchase. For example, the taxpayer holding shares may have bought shares each on five occasions, probably at a different price each time.
The individual lots of shares are typically not held separate; even in the days of physical stock certificatesthere was no indication which stock was bought when. If the taxpayer sells shares, then by designating which of the five lots is being sold, the taxpayer will realize one of five different capital gains or losses. The taxpayer can maximize or minimize the gain depending on an overall strategy, such as generating losses to offset gains, or keeping the total in the range that is taxed at a lower rate or not at all.
To use this strategy, the taxpayer must specify at the time of a sale which lot is being sold creating a "contemporaneous record". This "versus purchase" sale is versus against a specified purchase. On brokerage websites, a "Lot Selector" may let the taxpayer specify the purchase to which a sell order corresponds.
The two years of residency do not have to be continuous. An individual may meet the ownership and use tests during different 2-year periods. A taxpayer can move and claim the primary-residence exclusion every two years if living in an area where home prices are rising rapidly.
The tests may be waived for military service, disability, partial residence, unforeseen events, and other reasons.
Moving to shorten one's commute to a new job is not an unforeseen event. The amount of this exclusion is not increased for home ownership beyond five years.
Taxpayers can defer capital gains taxes to a future tax year using the following strategies: InPresident Barack Obama signed Executive Order establishing the National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform the "Simpson-Bowles Commission" to identify "policies to improve the fiscal situation in the medium term and to achieve fiscal sustainability over the long run".
The overview in the Commission's final report described its recommendations on taxes as to "Sharply reduce rates, broaden the base, simplify the tax code, and reduce the deficit by reducing the many 'tax expenditures'—another name for spending through the tax code.
Reform corporate taxes to make America more competitive, and cap revenue to avoid excessive taxation. Supporters described it as a "compromise" though "Anyone The Commission's tax proposals were not enacted.
Republicans, who did not control the Senate, wanted Obama to rally his fellow Democrats on fiscal policy; presidential candidate Mitt Romney faulted Obama for "missing the bus" on his own Commission.
Tax policy was a part of the presidential campaignas candidates proposed changes to the tax code that affect the capital gains tax.
President Donald Trump 's main proposed change to the capital gains tax was to repeal the 3. He also proposed to repeal the Alternative Minimum Taxwhich would reduce tax liability for taxpayers with large incomes including capital gains. Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton proposed to increase the capital gains tax rate for high-income taxpayers by "creating several new, higher ordinary rates", [66] and proposed a sliding scale for long-term capital gains, based on the time the asset was owned, up to 6 years.
The Republican Party introduced the American Health Care Act House Billwhich passed the House in May It would amend the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act "ACA" or "Obamacare" to repeal the 3. On April 26, Trump issued a one-page memorandum on tax reform. It contained no additional specifics on capital-gains taxation. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. This article is about Capital gains tax in the United States. For other countries, see Capital gains tax.
Alternative minimum tax Capital gains tax Corporate tax Estate tax Excise tax Gift tax Income tax Payroll tax Internal Revenue Service IRS Internal Revenue Code IRC IRS tax forms Revenue by state History Constitutional authority Taxpayer standing Court Protest Evasion.
State and local taxation. State income tax Property tax Sales tax Use tax Land value tax State tax levels. Automated payment transaction tax 9—9—9 Competitive Tax Plan Efficient Taxation of Income FairTax Flat tax Hall—Rabushka flat tax Kemp Commission Taxpayer Choice Act USA Tax Value added tax Border-adjustment tax. What's New for ?
Clifton Fleming; Peroni, Robert J. Doctrine, Structure, and Policy: Ebel, and Jane G. A Call for a More Responsible Approach to Investment and Business Management" PDF.
How Do I Figure Capital Gains Tax on Real Estate? | Home Guides | SF Gate
Spending and Revenue Options" PDF. Private Equity and Hedge Funds After the Global Financial Crisispage Marois; Cristina Alesci The New York Times. Past, Present, and Future". Capital Gain Rate Among World's Highest but President Obama Wants More". House Committee on Ways and Means and the Senate Committee on Finance. La Jeunesse July Is It Real and Is It a Puzzle?
Louis Federal Reserve Bank. An Economic Analysis of the Top Tax Rates Since " PDF. Archived from the original PDF on Lessons from the Tax Reform Act of ". Retrieved April 28, Retrieved March 7, Retrieved from " https: Taxation in the United States Capital gains taxes Investment in the United States. Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in.
Views Read Edit View history. Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Tools What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Wikidata item Cite this page. This page was last edited on 6 Juneat Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. This article is part of a series on. Federal taxation Alternative minimum tax Capital gains tax Corporate tax Estate tax Excise tax Gift tax Income tax Payroll tax Internal Revenue Service IRS Internal Revenue Code IRC IRS tax forms Revenue by state History Constitutional authority Taxpayer standing Court Protest Evasion.
State and local taxation State income tax Property tax Sales tax Use tax Land value tax State tax levels. Federal tax reform Automated payment transaction tax 9—9—9 Competitive Tax Plan Efficient Taxation of Income FairTax Flat tax Hall—Rabushka flat tax Kemp Commission Taxpayer Choice Act USA Tax Value added tax Border-adjustment tax.