How to compute cost of preferred stock
The cost of preferred stock is equal to the preferred dividend divided by the preferred stock price, plus the expected growth rate. A broad group of securities that pay a predictable fixed or floating rate of return or dividend until a certain date, at which point the holder has a number of options including converting the securities into the underlying share.
Preferred stock is an equity security with properties of both an equity and a debt instrument. It is generally considered a hybrid instrument.
How to Calculate the Cost of Preferred Stock
Preferred stock represents some degree of ownership in a company, but usually doesn't come with the same voting rights. In the event of liquidation , preferred shareholders are paid off before the common shareholder, but after debt holders. Preferred stock may also be callable or convertible, meaning that the company has the option to purchase the shares from shareholders at anytime for any reason - usually for a premium - or convert the shares to common stock.
Similar to bonds , preferred stocks are rated by the major credit rating companies. Some people consider preferred stock to be more like debt than equity. Because preferred stock carries a differing amount of risk than other types of securities, we must calculate its asset specific cost of capital to work into our overall weighted average cost of capital.
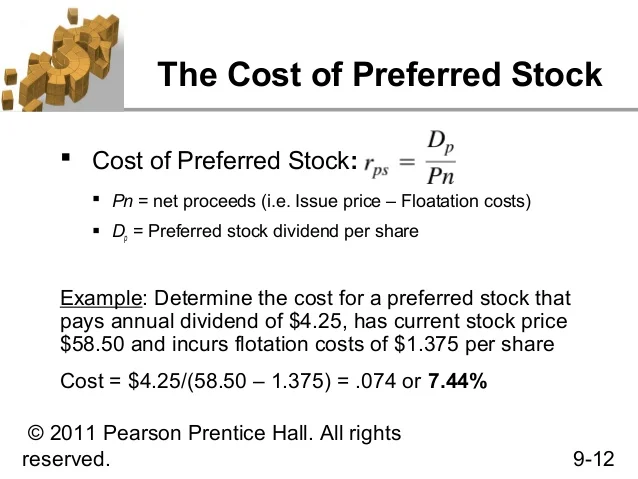
Similar to debt, this can be a relatively simple process since we can observe values needed as inputs in the market. With preferred shares , investors are usually guaranteed a fixed dividend forever. This is different than common stock, which has variable dividends that are never guaranteed. If preferred dividend is known and fixed, we can use the following equation to calculate the cost of capital for preferred stock.
The cost of preferred stock is equal to the preferred dividend divided by the preferred stock price, plus the growth rate.
This tells us that the cost of preferred stock is equal to the preferred dividend divided by the preferred stock price, plus the expected growth rate. The dividend is usually specified as a percentage of the par value or as a fixed amount.

Sometimes, dividends on preferred shares may be negotiated as floating - they may change according to a benchmark interest rate index. Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:. Except where noted, content and user contributions on this site are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.
Introduction to the Cost of Capital. Read Feedback Version History Usage. Learning Objective Calculate the cost of a company preferred stock. Key Points Preferred stock is an equity security with properties of both an equity and a debt instrument.
The Cost of Preferred Stock Preferred stock is an equity security with properties of both an equity and a debt instrument. Contribution To Cost of Capital Because preferred stock carries a differing amount of risk than other types of securities, we must calculate its asset specific cost of capital to work into our overall weighted average cost of capital.
Cost of Preferred Stock The cost of preferred stock is equal to the preferred dividend divided by the preferred stock price, plus the growth rate. Prev Concept The Cost of Debt. The Cost of Common Equity.
What Is the Formula to Calculate the Cost of Preferred Stock? -- The Motley Fool
What is the cost of the company's preferred stock? Key Term Reference Assets Appears in these related concepts: Unsecured Funding , Defining Long-Lived Assets , and Defining the Marketing Objectives. Common stock Appears in these related concepts: Common and Preferred Stock , Claim to Income , and Market Reporting. Interest Appears in these related concepts: Interest Compounded Continuously , Accounting for Interest Earned and Principal at Maturity , and Tax Considerations.
Preferred Stock Appears in these related concepts: Preferred Stock Rules and Rights , Voting Right , and Equity Finance.
Preferred dividends Appears in these related concepts: Liquidation Preference , Dividend Preference , and Ratio Analysis and EPS. Stock Appears in these related concepts: Ownership Nature of Stock , Advantages of Private Financing , and Financial Instruments. Voting rights Appears in these related concepts: Control and Preemption , Managers, Shareholders, and Bondholders , and Accounting for Preferred Stock.
Goodwill Impairment , Shifts in the Money Demand Curve , and Balance Sheets. Introduction to Corporate Social Responsibility , Measuring Organizational Performance , and Short-Term Loans. Factors Affecting the Price of a Bond , Current Maturities of Long-Term Debt , and Preferred Stock.
Maturity Date , Yield to Maturity , and Classifying Liabilities. Temple Architecture in the Greek Orientalizing Period , Minoan Architecture , and The Acropolis. Advantages of the Payback Method , Calculating the IRR , and Cost of Capital Considerations.
Honor and Violence , The Post-Closing Trial Balance , and Developing Services. Bond Rating System , Evaluating Interest Rates , and Answers to Chapter 10 Questions. Debt Utilization Ratios , Deficit Spending, the Public Debt, and Policy Making , and Collection from Delinquent Payables. Defining Dividends , Investor Preferences , and Division and Factors.
Motivating and Compensating Salespeople , Civil Law and Criminal Law , and The Psychology of Employee Satisfaction. The Valuation of Stocks , Calculating Perpetuities , and Discounted Dividend vs. Greenspan Era , The Financial Account , and Determinants of investment. Formation of the Corporation , Agency , and The United States Banking System. Liquidation , Bankruptcy and Bond Value , and Convertible Stock.
Characteristics of Bonds , Call Provisions , and Repurchasing Stock. Bonds Issued at Par Value , Accounting for Sale of Stock , and Par Value.
Common Stock , Issuing Stock , and Dividend Yield Ratio.
Cost Of Debt And Preferred Stock
The Term Structure , Redeeming Before Maturity , and Health Insurance. The Export-Import Bank of the United States , Approaches to Assessing Risk , and Risks Involved in Capital Budgeting. Secondary Market Organizations , Types of Market Organizations , and Seasoned Equity Offering. Advantages of Public Financing , Pricing a Security , and Underwriter. Defining Management , Arguments for and against Corporate Social Responsibility , and Types of Stakeholders. What is a Linear Function?

Calculating Expected Portfolio Returns , Average Cost Method , and Expected Value. Sources Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: Subjects Accounting Algebra Art History Biology Business Calculus Chemistry Communications Economics Finance Management Marketing Microbiology Physics Physiology Political Science Psychology Sociology Statistics U.
History World History Writing. Products For Students For Educators For Institutions Quizzes Integrations. Boundless About Us Approach Partners Press Community Accessibility. Follow Us Facebook Twitter Blog. Visit Support Email Us. Legal Terms of Service Privacy.